What is SD-WAN? Definition, principles and benefits
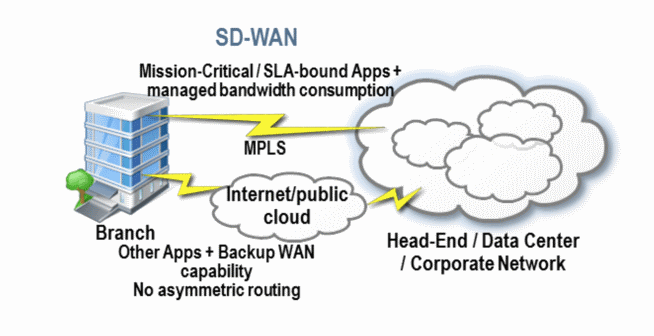
Why rethink the WAN and enterprise network architectures when MPLS has proven itself over the past 20 years? In recent years, CIOs and network managers have seen changes in the use and management of networks that have prompted them to think about adopting SD-WAN solutions to meet the new challenges of Enterprise 2.0.
First of all, the improvement of the Public Internet and the technological evolutions (4G, 5G, LTE...) make it possible for companies to change their strategy to reduce connection costs without sacrificing the performance of the services delivered.
Then there is the move of applications to the cloud, the use of SaaS solutions, or the centralization of applications with access to private datacenters. Office365, SalesForce, Cisco WebEx...
In addition, the organization of companies, the adaptability to business needs means that the IT department must adapt to changes in the way of working: WiFi, Smartphones, site opening, takeovers and business integrations...
Thus the network has to absorb the increase in bandwidth consumption from workstations and remote sites for new uses and to meet the needs of business adaptability.
1) Definition: What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN, Software Defined - Wide Area Network, was first defined by UNOG (Open Networking User Group) in 2014. The objective of this organisation was to implement a new WAN architecture in which the traditional private WAN connection is complemented by another Internet connection at a remote site, in order to reduce the costs associated with the WAN and increase the network management functionalities.
Thus, this additional connection fulfilled two main objectives:
- Gain direct access to applications hosted in the cloud, SaaS, etc.
- To have a second link between a remote site and the main site / datacenter of the company.
The additional connection is made through a secure tunnel allowing dynamic routing of applications based on link performance and link usage.
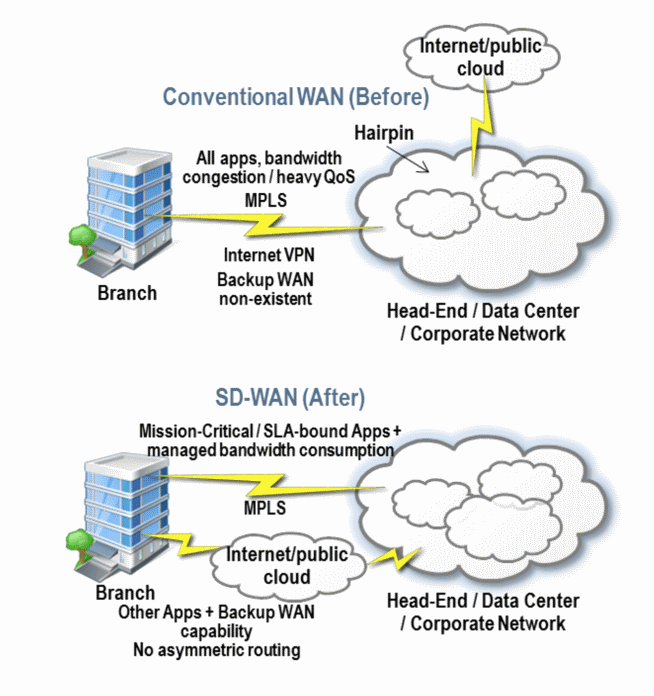
According to UNOG, this readjustment of network architectures can reduce overall connection costs while maintaining control over SLAs.
The role of the router evolves with SD-WAN: from simple routing and packet transfer, the router is responsible for the dynamic routing of applications to guarantee performance and security.
A single box can thus support several network functionalities, manage failover in a pool of connections including the public Internet and better control the costs of links/connections.
2) SD-WAN usage: Use cases
Here are the problems that SD-WAN is trying to solve:
High CapEx and OpEx of links and device stacks
- Cost of the circuit
- Management, visibility and control of WAN devices and bandwidth
- Connection between the Datacenter and remote sites
- No WAN bandwidth pooling agreement with x service providers
Open Networking Components:
- Open programming of remote site routers
- Centralized overlay of SDN controllers
- Remote site white box devices
Advantages observed when using SD-WAN:
- Mitigate asymmetrical routing
- Management of flows and use of the WAN as a multi-vendor bandwidth pool
- CapEx & OpEx - Reducing device stacking and circuit cost
- Supervision of links and applications directed over the WAN
- SLA-related applications over high-performance WANs and less critical applications over the Internet (VPN)
- Independent access, 3/4G, Broadband, Metro Ethernet, Fibre, etc.
3) The 10 criteria for an SD-WAN solution according to UNOG
According to the UNOG working group on SD-WAN, 10 points are listed for the "requirements" of an SD-WAN solution:
- Management of several active links (public and private)
- WAN built on physical and virtual equipment
- Secure hybrid WAN allowing application traffic engineering to be applied on a per-application basis, taking into account link performance.
- Visibility and prioritization of critical and real-time applications according to defined rules
- Highly redundant architecture
- Interoperability at levels 2 and 3 with the rest of the infrastructure
- Centralized management interface with dashboards per application, site and VPN
- Infrastructure Programmable with APIs on a controller that provides an abstraction of the whole. Sending logs to third party collectors (SIEM...)
- A device must be able to be deployed without configuration and with a minimum of effort in the current infrastructure.
- FIPS-140-2 certification for encryption
4) Points of vigilance in SD-WAN deployments
Beyond the improvements and developments brought by SD-WAN manufacturers and market players, certain points must continually require particular vigilance according to the particularities of each information system and the specific business needs of each company:
- Cost (ROI varies from one organization to another)
- Security (Management of remote sites and remote connections)
- Cloud (Deployment mode according to the company's criteria: Cloud / Hybrid / On-site)
- Migration (Existing, Migration, Transition, Adaptation, Exceptions...)
5) Evolutions and virtualization of network functions at remote sites
In order to simplify networks as much as possible and avoid the stacking of "boxes", one option that is increasingly being considered is total virtualization of network functions (NFV) at remote sites. Thus, a single x86 server is installed (or several servers in the case of highly redundant architectures) with all the expected functions virtualized on this infrastructure.
This can have several advantages:
- The deployment of a new function does not require any logistic operation, nor any costly manual installation operation. Simply load the virtual appliance at the remote site and a new feature can be available in a very short period of time.
- The network architecture and design are simplified since there is no longer any physical constraint to connect equipment. If it is necessary to modify or adapt a network infrastructure (for example to place the IPS upstream of the WAN optimization) this can be done in a few clicks without rewiring.
6) Challenges and management of x86 servers and NFV function
There are of course particularities to consider whether it is hardware, software, organizational or orchestration depending on the remote sites:
- Server format (remote sites are not datacenter clean rooms, noise, shock resistance, air conditioning...)
- WAN connectivity (Datacenter connectivity, LTE, Fibre, DSL...)
- Ease of deployment (no manual operation other than a few electrical and network connections)
- Performance (Analysis and optimization of inter-server / inter-VM flows, analysis of traffic between remote sites and the datacenter)
- Management (Management of hypervisor, latency, redundant architectures)
- Integration into the existing IT and network ecosystem (management of existing systems, integration of SNMP network management protocols, syslog...)
Conclusion regarding network virtualization functions
Thus, thanks to the network virtualization (NFV) functions, many market players now offer SD-WAN solutions based on the use of a single server / box grouping together all the equipment, network functions (security, routing, automatic failover, etc.) and the majority of business IT needs.
These make it possible to simplify the networks and their management to the maximum as well as to accelerate the agility of solution deployments to meet business needs or new uses.
On the other hand, SD-WAN enables better control over connection costs (telecom in particular), as well as better management of connection pools (multi-media and WAN via Public Internet).
It is therefore advisable to consider how SD-WAN can be integrated into the current well-established operational processes and make a transition in accordance with business needs, the IT department's strategy, the existing situation and the specific features of certain sites.
Sources:
- "Le SD-WAN pour les nuls". Jérôme Durand: https://conf-ng.jres.org/2017/document_revision_2938.html?download
