What is Generic Application Trace Monitoring?
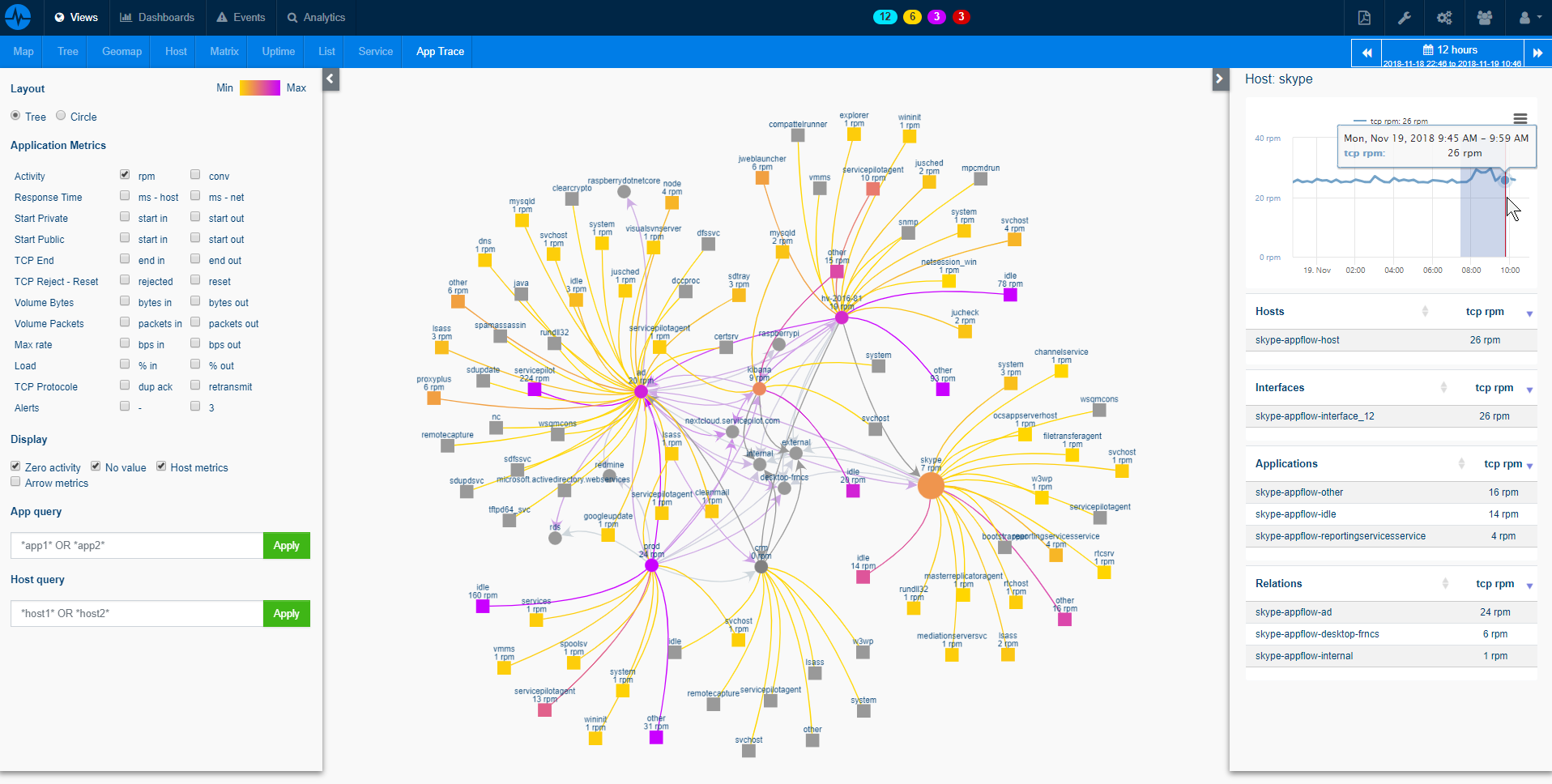
ServicePilot's Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and distributed tracing capabilities provide deep insight into how application services behave. Whether monolithic or built on microservices, standard intuitive dashboards allow to surface critical performance data like latency, error rates and throughput.
The generic AppTrace AppService package is designed to collect distributed traces from any instrumented application covering many languages and databases. This includes applications written in: .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, PHP, Ruby, Go and other application languages that support instrumentation with OpenTelemetry, OpenTracing, Zipkin or dd-trace API libraries.
Generic Application Trace Monitoring
Generic AppTrace AppService enables the monitoring of HTTP(S) request traces from instrumented applications.
The ServicePilot Agent captures trace data (via ServicePilot, OpenTelemetry, OpenTracing, Zipkin or dd-trace API instrumentation) and relays it to ServicePilot, where it's stored, structured into metrics and displayed in application-centric dashboards.
It supports web services, APIs, background tasks, different databases, containerized, serverless and/or traditional server-based deployments.
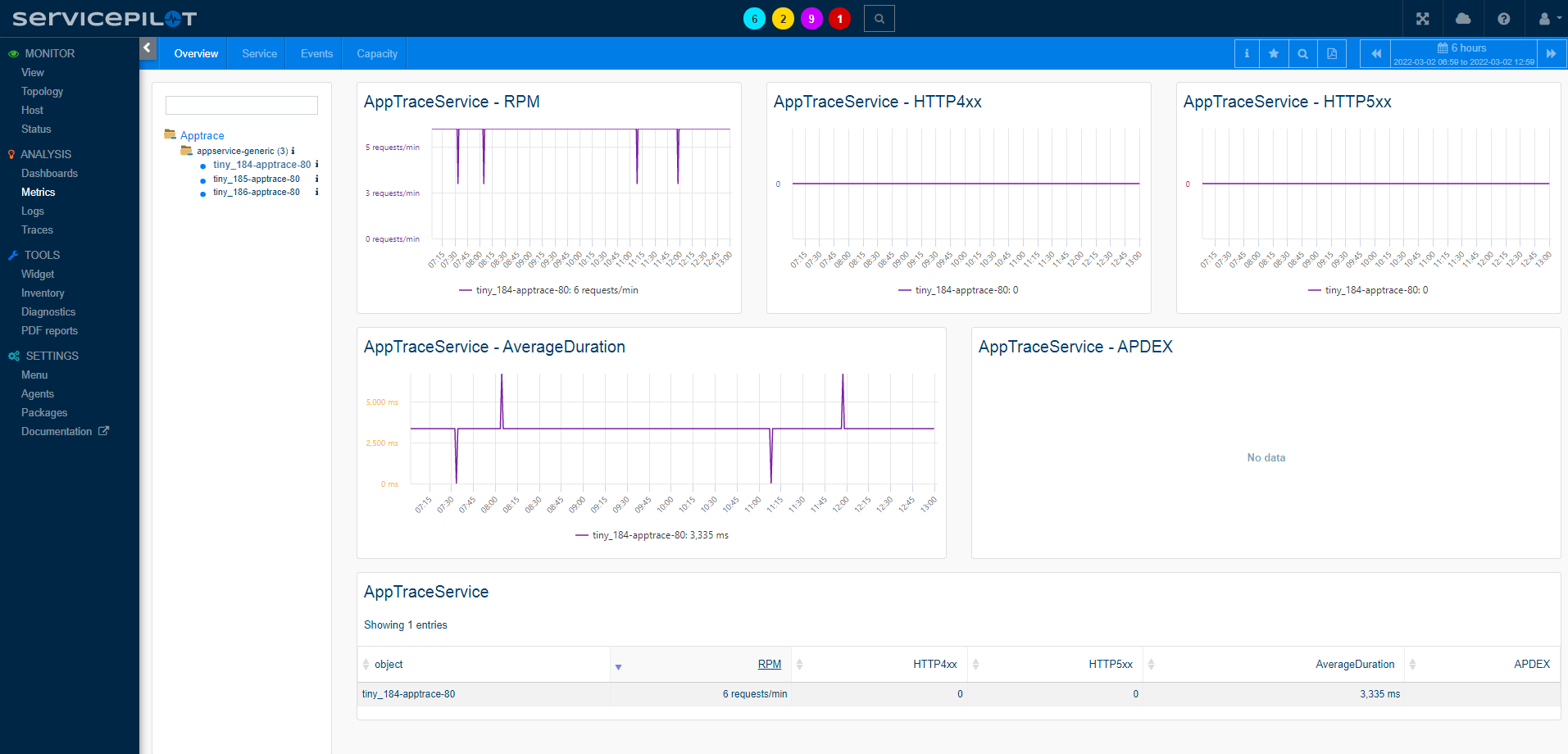
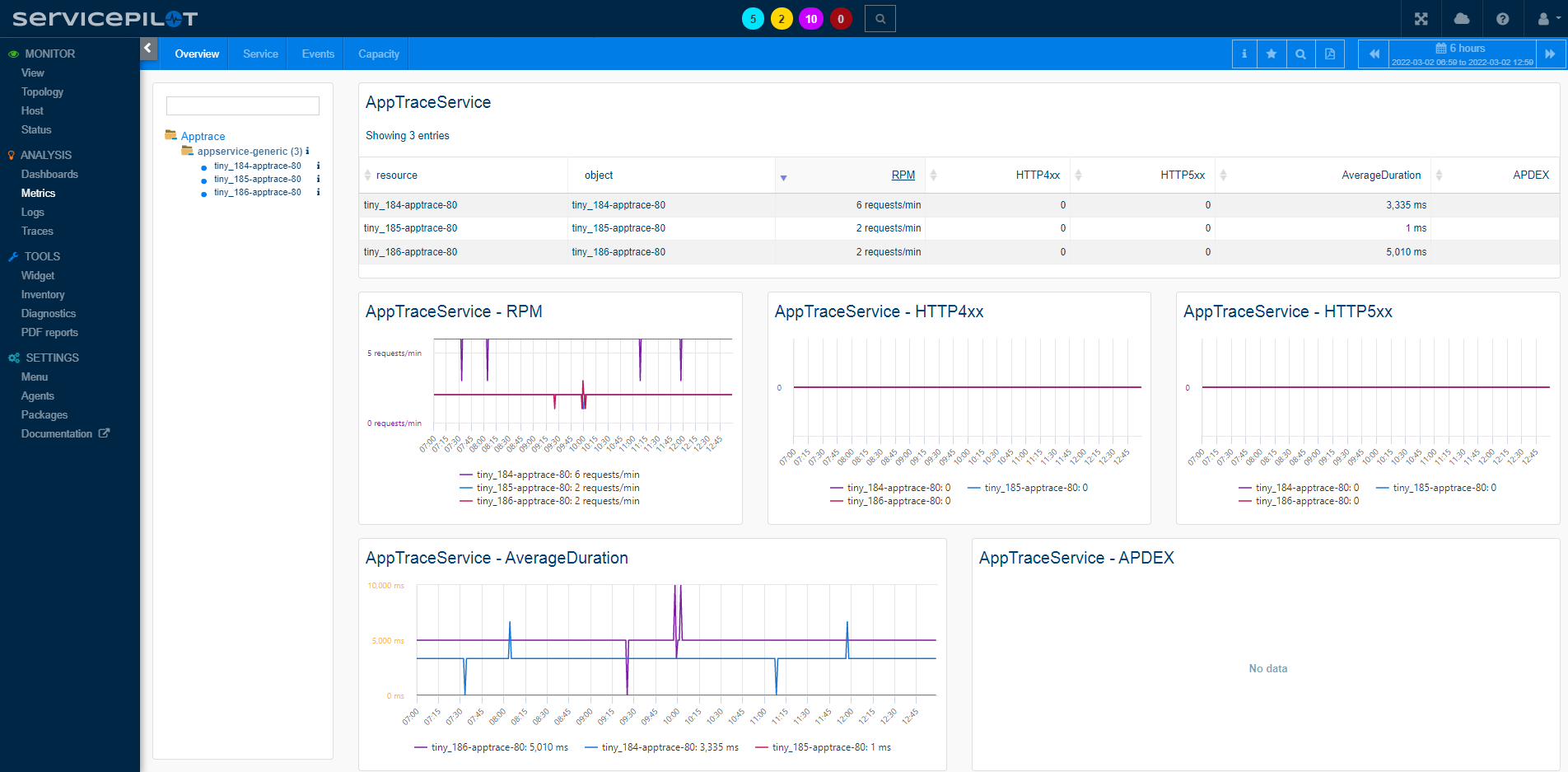
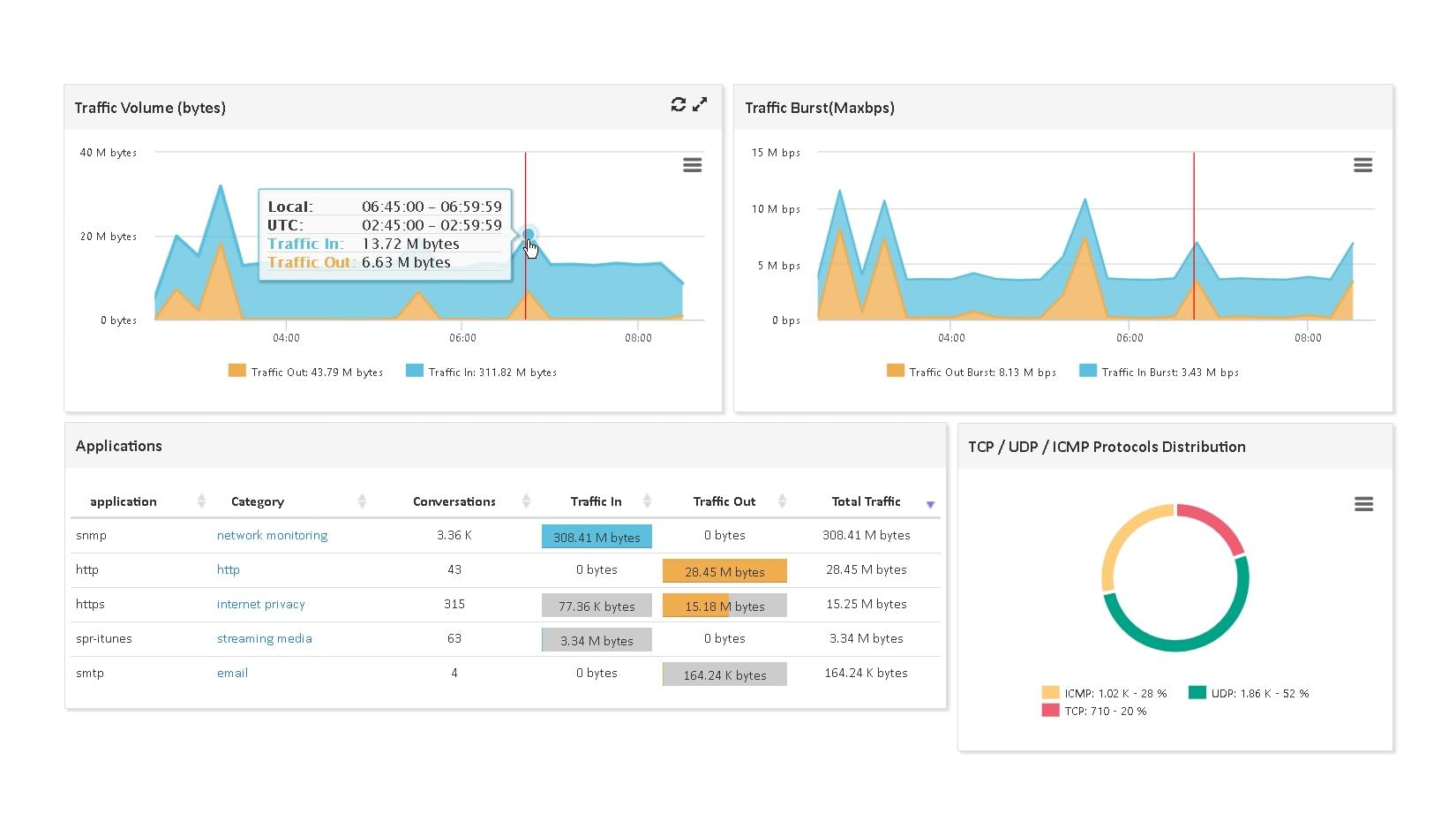
For each instrumented application, ServicePilot collects aggregated statistics (min,max,avg...) such as:
- Requests per minute
- HTTP method and return code breakdowns
- Latency distribution (fast, moderate, slow, very slow, timed-out)
- Established vs. timed-out connections
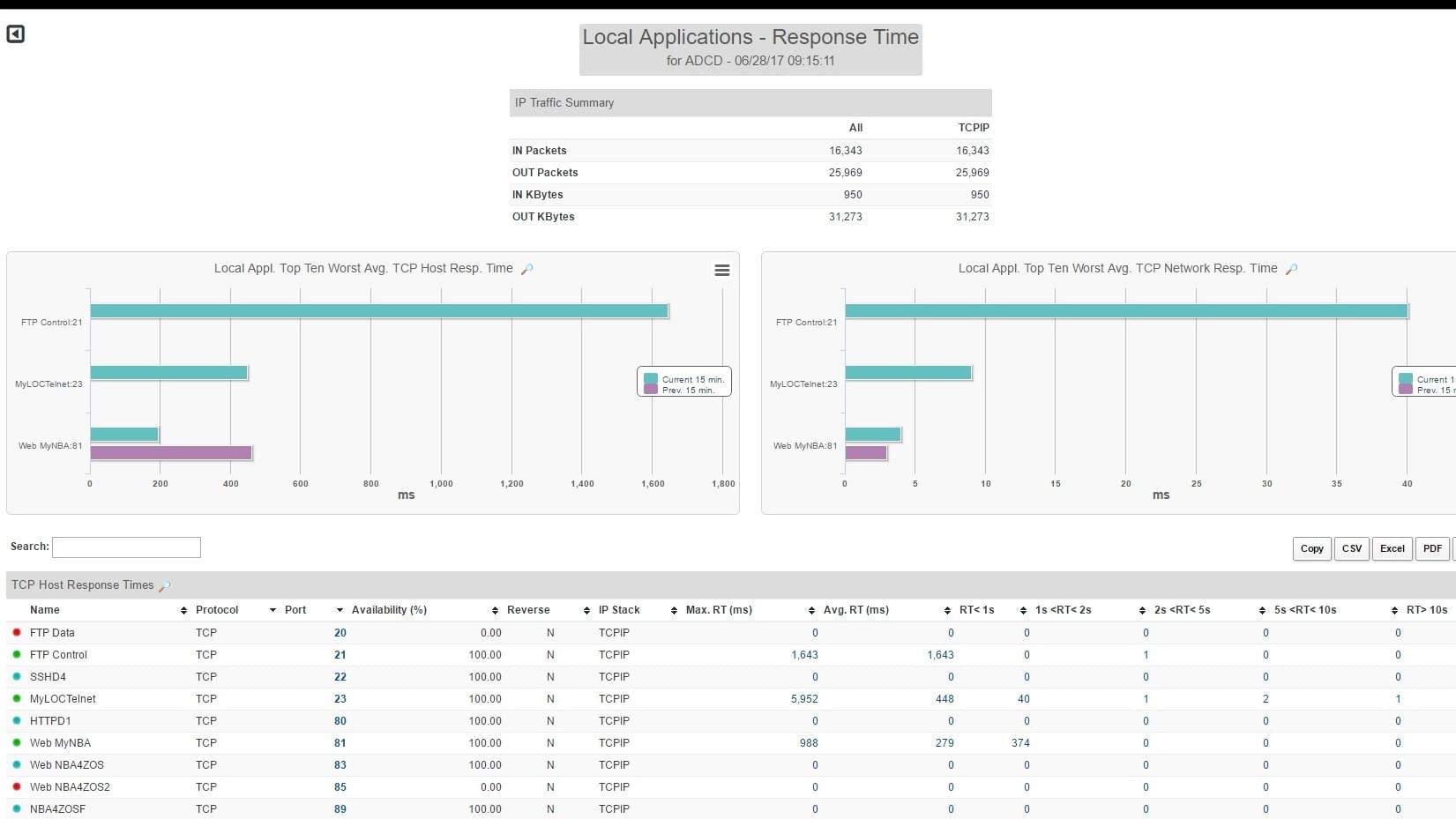
Per-Request details collected include:
- Client IP and geolocation (for public IPs)
- Host, URI path and full URL
- HTTP Method and Status Code
- User Response Time
- RUM (Real User Monitoring) and Session Replay correlation with Tracing data
How to install a appservice resource?
- Use your ServicePilot OnPremise installation or a SaaS account.
- Add a new appservice resource via the web interface (
/prmviewsor/prmresources) or via API (/prmpackagespage), the default ServicePilot agent or another agent will be provisioned automatically.
Details of the appservice package are located in the
/prmpackagespage of the software.
Benefits
ServicePilot enables you to deliver IT services faster and more securely with automated discovery and advanced monitoring features.
By correlating the technology APPSERVICE with APM and infrastructure monitoring, ServicePilot is able to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's IT environment.
This allows IT teams to quickly identify and diagnose issues that may be impacting application performance, and take corrective action before end-users are affected.
Start with a free trial of our SaaS solution. Explore our plans or contact us to find what works best for you.