What is Kubernetes Inventory?
Kubernetes, also known as k8s or kube, is a powerful container orchestration platform. It automates the deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications, ensuring that they run efficiently and reliably.
A Kubernetes Inventory is a comprehensive record of all the resources within a Kubernetes cluster. This includes Nodes, Pod Containers, and Daemon Sets. Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date Kubernetes Inventory is crucial for several reasons:
- Reduction of inventory errors: An accurate inventory helps to prevent errors that can lead to downtime or inefficient resource utilization.
- Improved ability to meet customer demands: By knowing exactly what resources are available, organizations can better plan and allocate resources to meet customer needs.
- Lower operational costs: Efficient resource utilization can lead to significant cost savings.
How to monitor Kubernetes Inventory?
ServicePilot makes it easy to monitor a Kubernetes cluster by simply adding a ServicePilot Agent in a Pod as part of a DaemonSet. A corresponding resource of the server-kubernetes-inventory package then needs to be added via the ServicePilot web interface to receive information from the ServicePilot Agent.
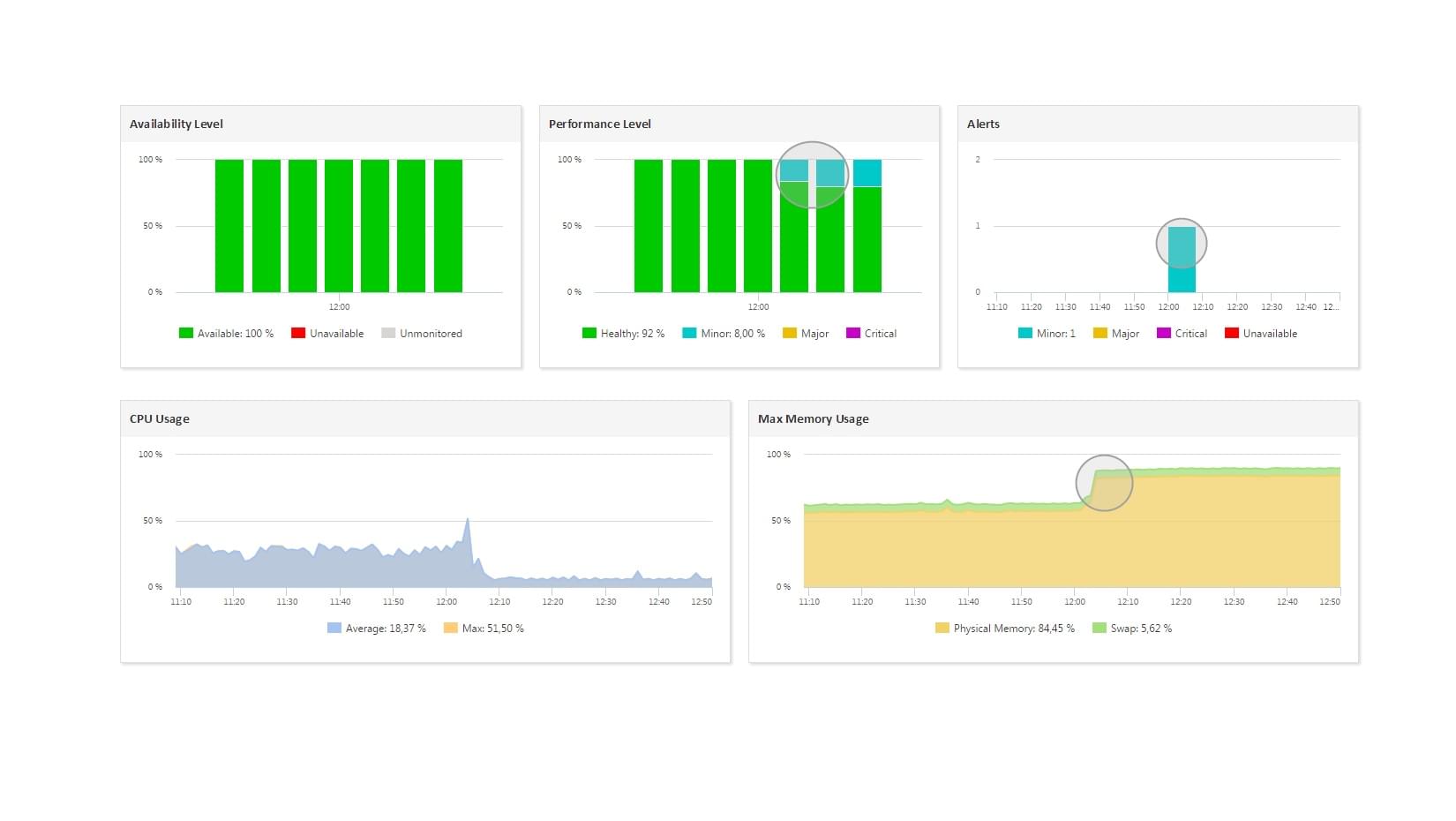
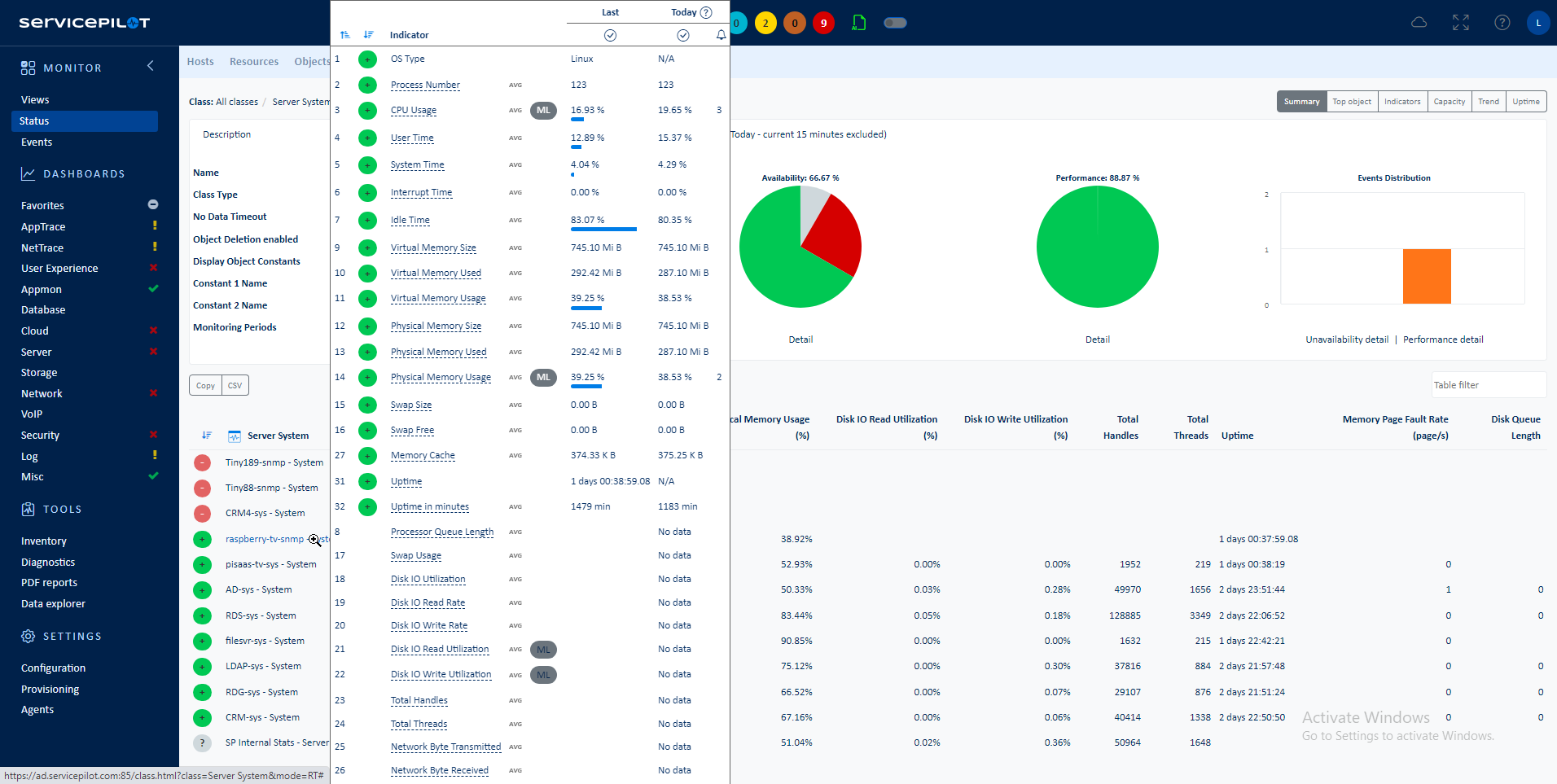
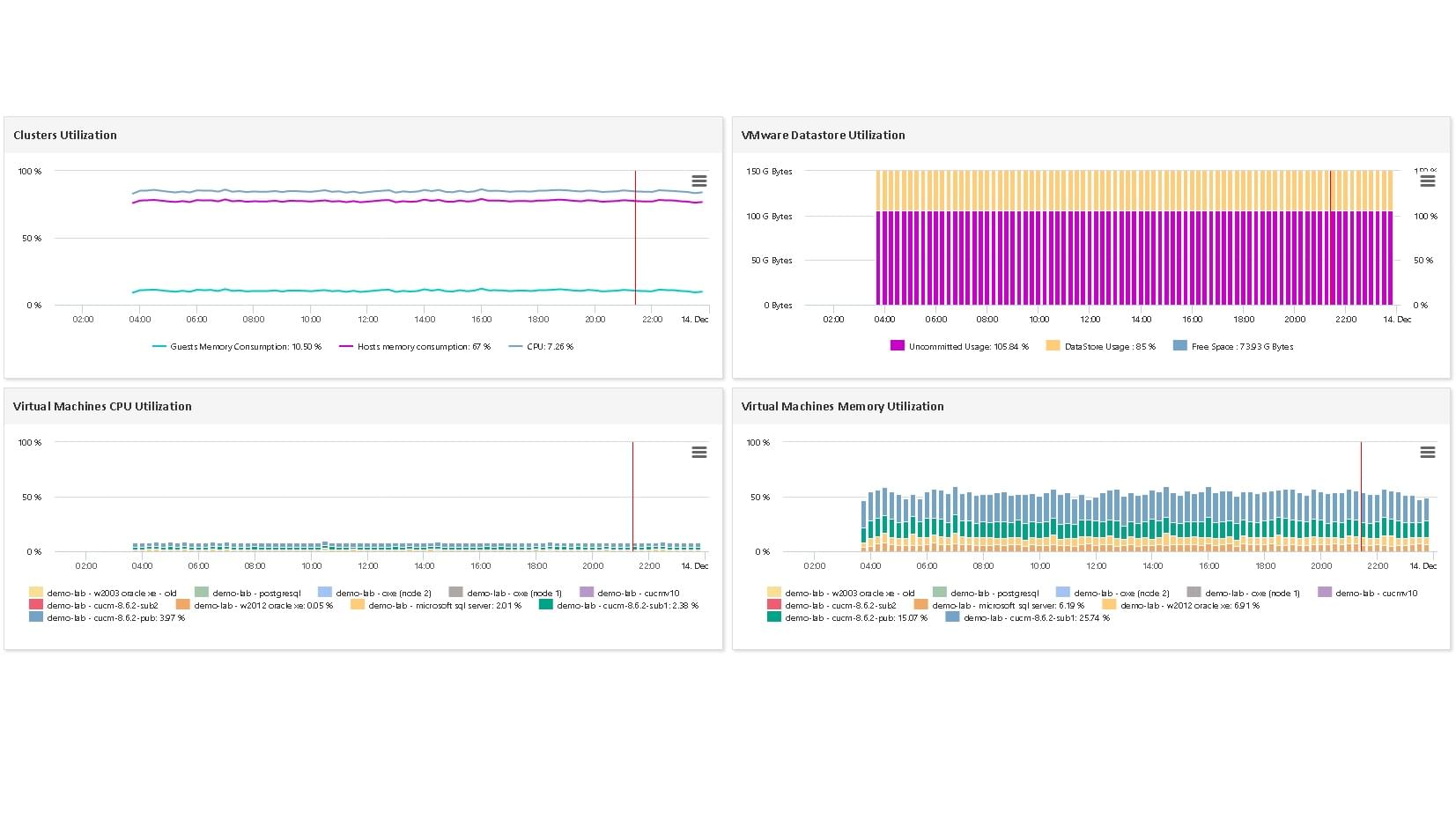
The monitoring statistics gathered in this way include:
- DaemonSet
- State and number of pods running the DaemonSet
- Deployments
- Replicas state
- Node
- Pods usage
- Memory usage
- CPU usage
- Pod Containers
- State
- Memory requests and limit
- Restarts
How to install a kubernetes-inventory resource?
- Use your ServicePilot OnPremise installation or a SaaS account.
- Add a new kubernetes-inventory resource via the web interface (
/prmviewsor/prmresources) or via API (/prmpackagespage), the default ServicePilot agent or another agent will be provisioned automatically.
Details of the kubernetes-inventory package are located in the
/prmpackagespage of the software.
Benefits
ServicePilot enables you to deliver IT services faster and more securely with automated discovery and advanced monitoring features.
By correlating the technology KUBERNETES INVENTORY with APM and infrastructure monitoring, ServicePilot is able to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's IT environment.
This allows IT teams to quickly identify and diagnose issues that may be impacting application performance, and take corrective action before end-users are affected.
Start with a free trial of our SaaS solution. Explore our plans or contact us to find what works best for you.