What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes — also known as k8s or kube — is a container orchestration platform for scheduling and automating the deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications.
Containers are similar to VMs, but they have relaxed isolation properties to share the Operating System (OS) among the applications. Therefore, containers are considered lightweight. Similar to a VM, a container has it's own filesystem, share of CPU, memory, process space, and more. As they are decoupled from the underlying infrastructure, they are more portable across clouds and OS distributions.
Containers have become popular because they provide extra benefits, such as:
- Agile application creation and deployment
- Continuous development, integration, and deployment
- Dev and Ops separation of concerns
- Observability
- Environmental consistency across development, testing, and production
- Cloud and OS distribution portability
- Application-centric management
- Loosely coupled, distributed, elastic, liberated micro-services
- Resource isolation: predictable application performance
- Resource utilization: high efficiency and density
Monitoring Kubernetes
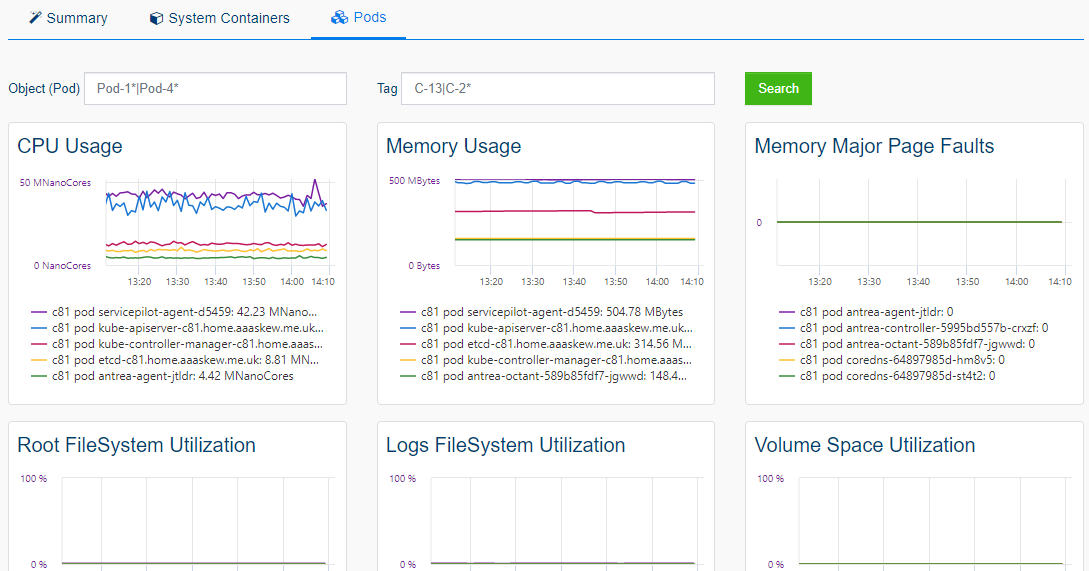
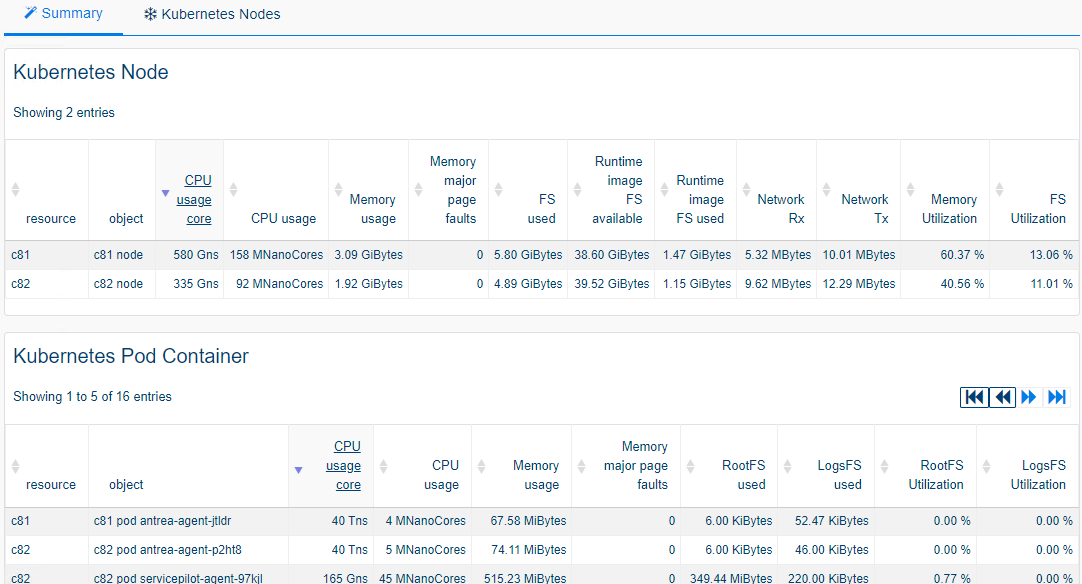
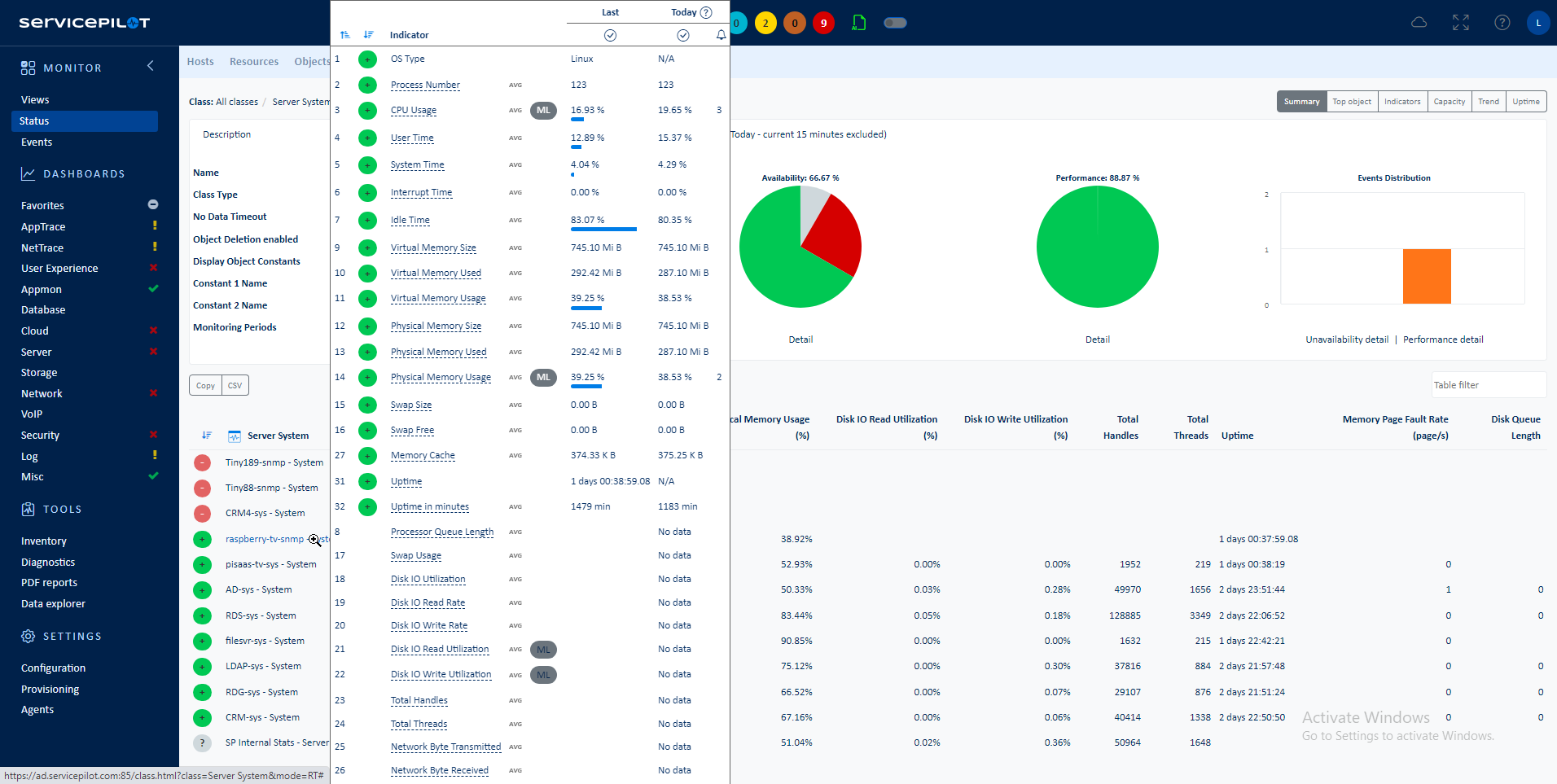
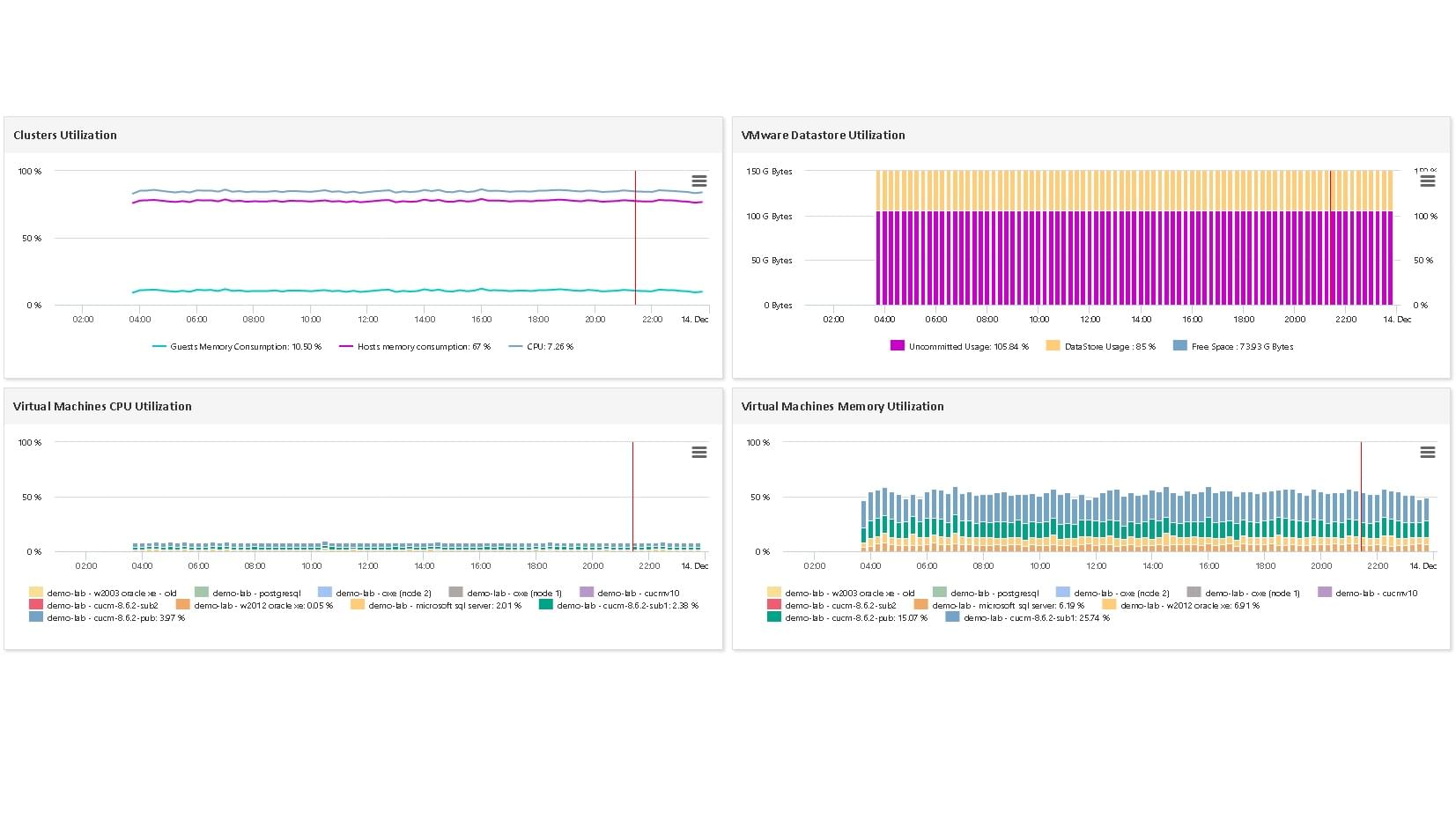
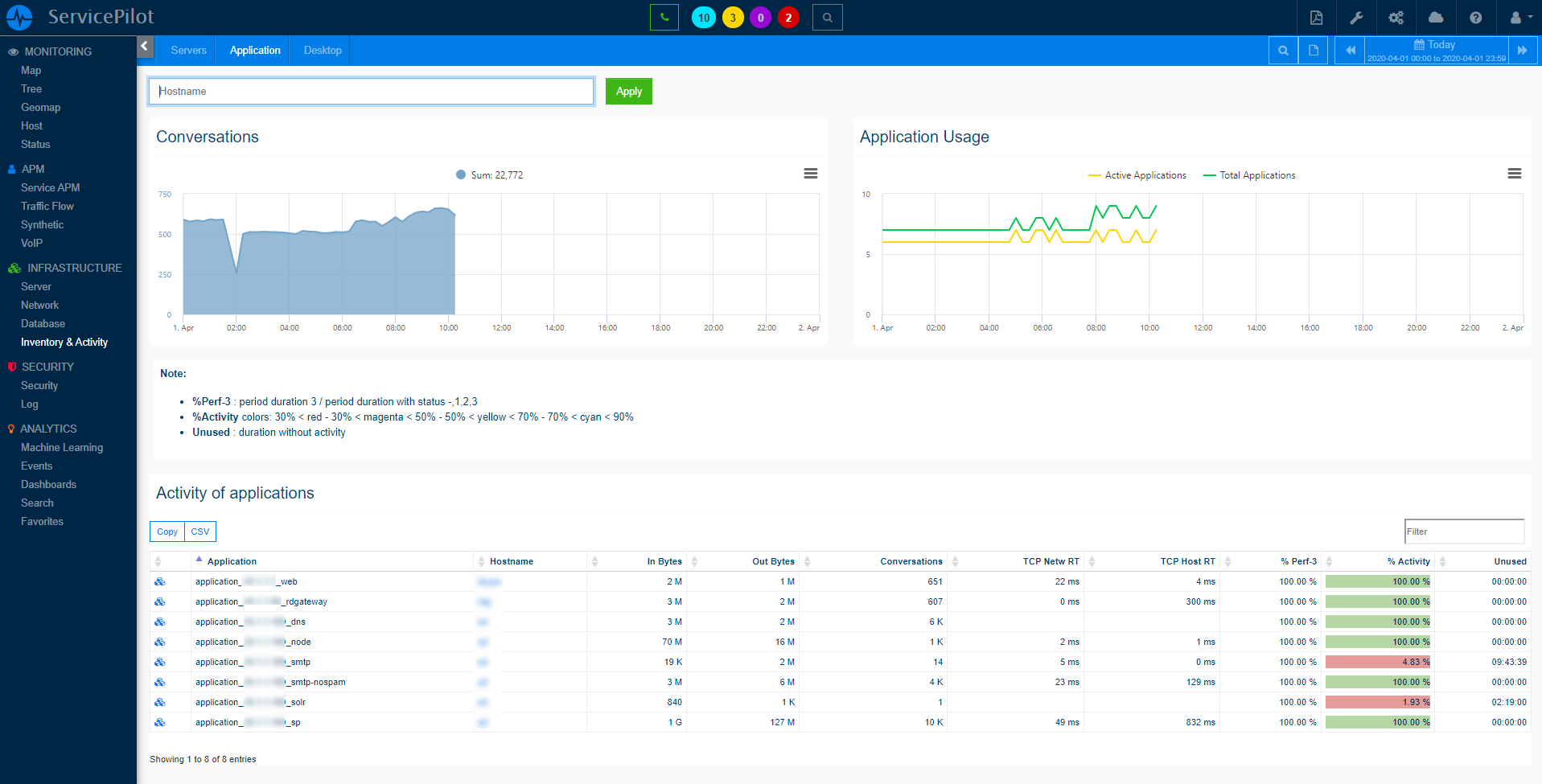
ServicePilot monitors a Kubernetes Node by communicating with the Kubelet API from a ServicePilot Agent installed in a Pod. It is assumed that ServicePilot Agents are running in Pods as part of a DaemonSet within a Kubernetes cluster so that each ServicePilot Agent can report on its Node statistics.
The statistics gathered in this way include:
- Node
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- File system usage
- Network usage
- System components
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- File system usage
- Pod
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- File system usage
- Network usage
- Pod volume usage
How to install a kubernetes resource?
- Use your ServicePilot OnPremise installation or a SaaS account.
- Add a new kubernetes resource via the web interface (
/prmviewsor/prmresources) or via API (/prmpackagespage), the default ServicePilot agent or another agent will be provisioned automatically.
Details of the kubernetes package are located in the
/prmpackagespage of the software.
Benefits
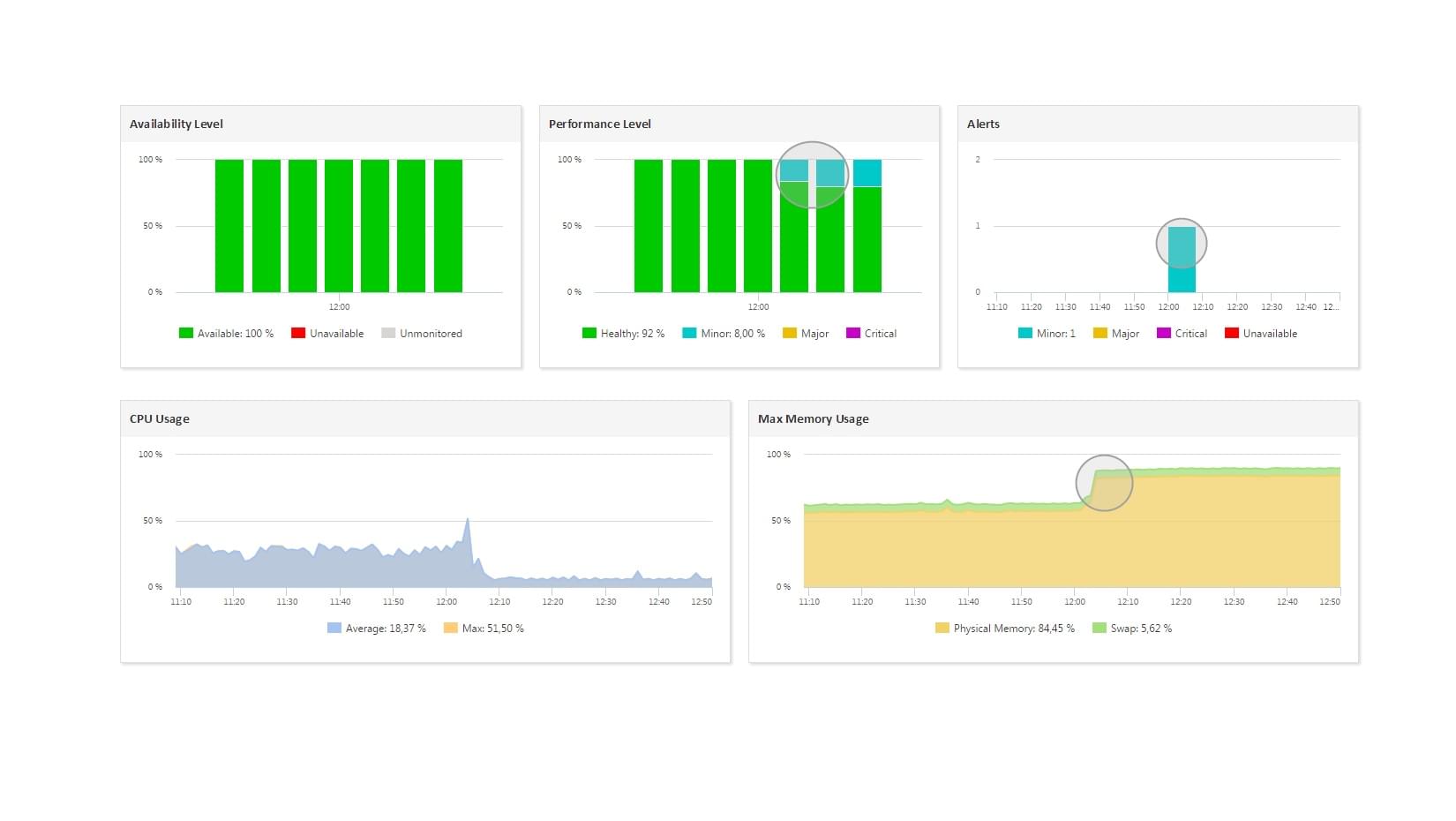
ServicePilot enables you to deliver IT services faster and more securely with automated discovery and advanced monitoring features.
By correlating the technology KUBERNETES with APM and infrastructure monitoring, ServicePilot is able to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's IT environment.
This allows IT teams to quickly identify and diagnose issues that may be impacting application performance, and take corrective action before end-users are affected.
Start with a free trial of our SaaS solution. Explore our plans or contact us to find what works best for you.